This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
Problem Set Master Index Study notes linked in blog: Binary Search Trees and AVL Trees
04-Tree 4 Is It the Same Binary Search Tree (25 pts)
The beginner's session will provide a detailed introduction to the C language implementation. This is basic training and must be done.
Problem Description
For various input insertion sequences, determine whether they generate the same binary search tree.
Approach
- Build two separate trees and compare them. 2. Directly determine from the sequences without building trees. 3. Build one tree and check whether other sequences are consistent with it. Here we use approach 3.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define maxsize 11
typedef struct TNode* Tree;
struct TNode {
int data;
Tree left,right;
int flag; //判断是否访问过
};
void Clear(Tree R) { //清除标记
if(!R) return;
R->flag = 0;
Clear(R->left);
Clear(R->right);
}
void FreeTree(Tree R) { //清空该树
if(!R) return;
FreeTree(R->left);
FreeTree(R->right);
delete R;
}
Tree NewNode(int data) {//
Tree R = new TNode;
R->data = data;
R->left = R->right = NULL;
R->flag = 0;
return R;
}
Tree BST_Insert(int data, Tree R) {
if (!R) R = NewNode(data);
else {
if(data > R->data) //大于该结点,插入到右子树
R->right = BST_Insert(data, R->right);
else //小于或等于该结点,插入到左子树
R->left = BST_Insert(data, R->left);
}
return R;
}
Tree Build(int N) {
Tree R = NULL;
int x;
cin >> x;
R = NewNode(x);
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> x;
R = BST_Insert(x, R);
}
return R;
}
bool check(int data, Tree R) {
if(R->flag) {//已经访问过了
if(data < R->data)
return check(data, R->left);
else if(data > R->data)
return check(data, R->right);
else return false;
} else {
if(data == R->data) {
R->flag = 1;
return true;
} else return false;
}
}
bool judge(Tree R1, int N) {
int x;
bool flag = true;
if(N && R1) {
cin >> x;
if(x != R1->data) flag = false;
R1->flag = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> x;
if(flag && (!check(x,R1))) flag = false;
}
}
return flag;
}
int main() {
int N, L;
cin >> N;
while(N) {
cin >> L;
Tree R1;
R1 = Build(N);
for(int i = 0; i < L; ++i) {
if(judge(R1, N))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
Clear(R1); //清除标记
}
FreeTree(R1);
cin >> N;
}
return 0;
}
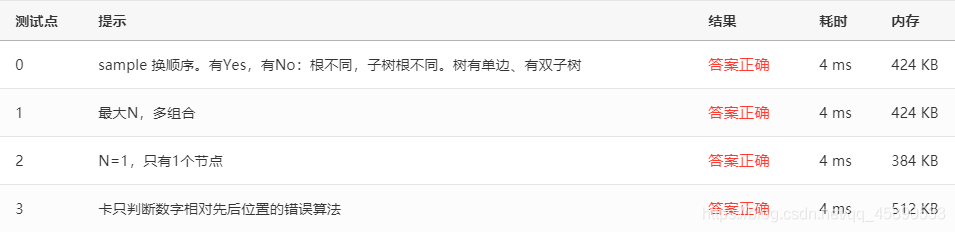
Test Cases
Test cases are as follows
04-Tree 5 Root of AVL Tree (25 pts)
This is a 2013 Zhejiang University Computer Science graduate admission exam problem. It is basic AVL tree training and must be done.
Problem Description
Given an insertion sequence, output the root of the generated AVL tree.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxsize 11
typedef struct AVLNode* AVLTree;
struct AVLNode {
int data;
AVLTree left,right;
int Height;
};
void FreeTree(AVLTree R) { //清空该树
if(!R) return;
FreeTree(R->left);
FreeTree(R->right);
delete R;
}
int GetHeight(AVLTree R) {
if(R)
return R->Height;
else
return 0;
}
AVLTree SingleLeftRotate(AVLTree R) { //LL单旋
AVLTree RL = R->left;
R->left = RL->right;
RL->right = R;
R->Height = max( GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right) ) + 1;
RL->Height = max( GetHeight(RL->left), R->Height) + 1;
return RL;
}
AVLTree SingleRightRotate(AVLTree R) { //RR单旋
AVLTree RR = R->right;
R->right = RR->left;
RR->left = R;
R->Height = max( GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right) ) + 1;
RR->Height = max( R->Height, GetHeight(RR->right) ) + 1;
return RR;
}
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotate(AVLTree R) { //LR旋转
R->left = SingleRightRotate(R->left);
return SingleLeftRotate(R);
}
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotate(AVLTree R) { //RL旋转
R->right = SingleLeftRotate(R->right);
return SingleRightRotate(R);
}
AVLTree NewNode(int data) {//
AVLTree R = new AVLNode;
R->data = data;
R->left = R->right = NULL;
R->Height = 0;
return R;
}
AVLTree AVL_Insert(int data, AVLTree R) {
if (!R) R = NewNode(data);
else if(data < R->data) { //插入到左子树
R->left = AVL_Insert(data, R->left);
if(GetHeight(R->left) - GetHeight(R->right) == 2) { //需要左旋
if (data < R->left->data)
R = SingleLeftRotate(R); //需要左单旋
else
R = DoubleLeftRightRotate(R);//左-右双旋
}
} else if(data > R->data) { //插入到右子树
R->right = AVL_Insert(data, R->right);
if(GetHeight(R->left) - GetHeight(R->right) == -2) { //需要右旋
if (data > R->right->data)
R = SingleRightRotate(R); //需要右单旋
else
R = DoubleRightLeftRotate(R);//右-左双旋
}
}
R->Height = max(GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right)) + 1;
return R;
}
AVLTree Build(int N) {
AVLTree R = NULL;
int x;
cin >> x;
R = NewNode(x);
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> x;
R = AVL_Insert(x, R);
}
return R;
}
int main() {
int N, L;
AVLTree R;
cin >> N;
R = Build(N);
cout << R->data << endl;
return 0;
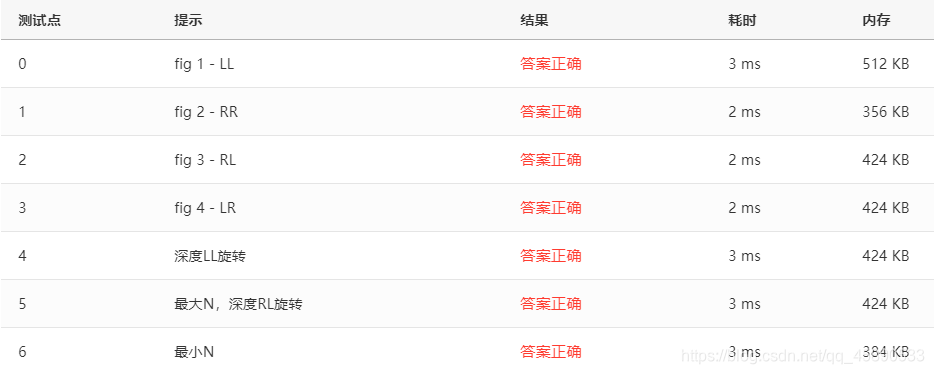
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows
04-Tree 6 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 pts)
This is a 2013 Fall PAT Level A exam problem. Somewhat challenging, proceed according to your ability. An explanation will be given in Week 7.
Problem Description
Given an insertion sequence for a complete binary search tree, output the level-order traversal sequence of the generated complete binary tree.
Approach
Since it is a complete binary search tree, by the property that left subtree values < root value < right subtree values, the given input sequence sorted in ascending order becomes the inorder traversal sequence of the tree. Then recursively construct the level-order traversal sequence from the inorder traversal result. In the inorder traversal sequence, when the total number of nodes is n and the left subtree has x nodes, the root is the (x+1)-th element. How do we know the number of left subtree nodes? This is determined by the properties of a complete binary tree -- for a complete binary tree with n nodes, the number of left subtree nodes is fixed. So we can create a function that calculates the number of left subtree nodes given the total number of nodes. The following binary tree properties are used:
- A binary tree with n nodes has depth log2(n) + 1
- Level i of a binary tree has at most 2i-1 nodes
- A binary tree of depth k has at most 2k-1 nodes
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxsize 2002
#define Null -1
int a[maxsize],b[maxsize];//中序遍历的结果 层次遍历的结果
int GetLeftSum(int n) { //获取左子树总结点数 n为结点总数
if(n == 1) return 0;
int h = log2(n);//除最后一层的深度
int Lsum = pow(2, h-1) - 1; //除最后一层之外的左子树结点个数
//即为(2^h-1-1)/2
int last = n - (pow(2, h) - 1); //最后一层结点数
if(last <= pow(2, h-1))
Lsum += last;
else Lsum += pow(2, h-1);
return Lsum;
}
void LevelOrderRebuild(int left, int right,int bR) {
int n = right - left + 1;//总结点数
if(n == 0) return;
int leftlen = GetLeftSum(n);
int aR = left + leftlen;
b[bR] = a[aR];
int nl = bR * 2 + 1;
int nr = nl + 1;
LevelOrderRebuild(left, aR-1, nl);
LevelOrderRebuild(aR+1, right, nr);
}
int main() {
int N;
cin >> N;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
sort(a, a+N);
LevelOrderRebuild(0, N-1, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if(i) {
cout << " " << b[i];
} else cout << b[i];
}
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows:
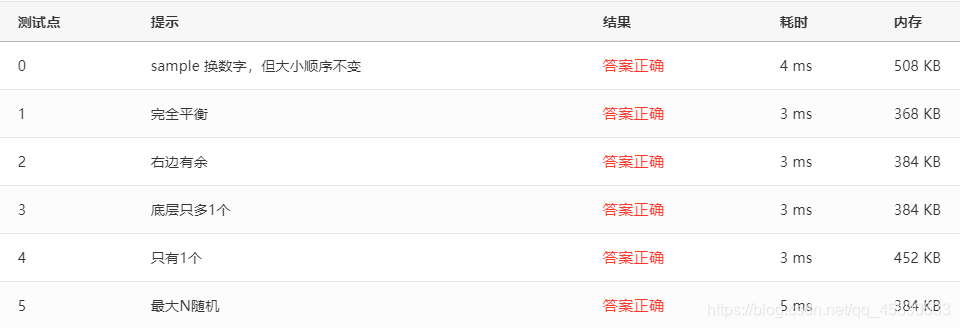
04-Tree 7 Binary Search Tree Operations (30 pts)
Problem Description
Implement the operation set for a binary search tree.

Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{
ElementType Data;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) { /* 先序遍历,由裁判实现,细节不表 */
if(BT) {
printf("%d", BT->Data);
PreorderTraversal( BT->Left);
PreorderTraversal( BT->Right);
}
}
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) { /* 中序遍历,由裁判实现,细节不表 */
if(BT) {
InorderTraversal( BT->Left);
printf("%d", BT->Data);
InorderTraversal( BT->Right);
}
}
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X );
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X );
Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X );
Position FindMin( BinTree BST );
Position FindMax( BinTree BST );
int main()
{
BinTree BST, MinP, MaxP, Tmp;
ElementType X;
int N, i;
BST = NULL;
scanf("%d", &N);
for ( i=0; i<N; i++ ) {
scanf("%d", &X);
BST = Insert(BST, X);
}
printf("Preorder:"); PreorderTraversal(BST); printf("\n");
MinP = FindMin(BST);
MaxP = FindMax(BST);
scanf("%d", &N);
for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) {
scanf("%d", &X);
Tmp = Find(BST, X);
if (Tmp == NULL) printf("%d is not found\n", X);
else {
printf("%d is found\n", Tmp->Data);
if (Tmp==MinP) printf("%d is the smallest key\n", Tmp->Data);
if (Tmp==MaxP) printf("%d is the largest key\n", Tmp->Data);
}
}
scanf("%d", &N);
for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) {
scanf("%d", &X);
BST = Delete(BST, X);
}
printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BST); printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) {
if(!BST) {
BST = (BinTree) malloc(sizeof(struct TNode));
BST->Data = X;
BST->Left = BST->Right = NULL;
return BST;
} else {
if(X < BST->Data)
BST->Left = Insert(BST->Left, X);
else if(X > BST->Data)
BST->Right = Insert(BST->Right, X);
}
return BST;
}
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) {
Position tmp;
if(!BST) printf("Not Found\n");
else if (X < BST->Data)
BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left, X);
else if (X > BST->Data)
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, X);
else { //找到了要删除的结点
if (BST->Left && BST->Right) { //待删除结点有左右两个孩子
tmp = FindMin(BST->Right); //在右子树中找最小的元素填充删除节点
BST->Data = tmp->Data;
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, tmp->Data);
//填充完后,在右子树中删除该最小元素
}
else { //待删除结点有1个或无子结点
tmp = BST;
if (!BST->Left) //有有孩子或无子节点
BST = BST->Right;
else if (!BST->Right)
BST = BST->Left;
free(tmp);
}
}
return BST;
}
Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) {
while (BST) {
if(X < BST->Data)
BST = BST->Left;
else if(X > BST->Data)
BST = BST->Right;
else return BST;
}
return NULL;
}
Position FindMin( BinTree BST ) {
if(BST) {
while(BST->Left)
BST = BST->Left;
}
return BST;
}
Position FindMax( BinTree BST ) {
if(BST) {
while(BST->Right)
BST = BST->Right;
}
return BST;
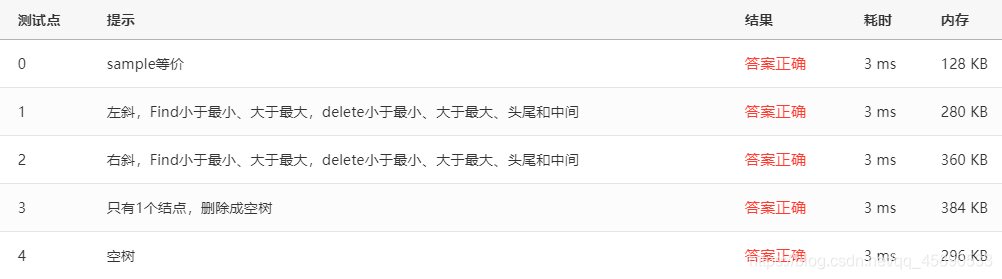
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~