This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
Problem Set Master Index Study notes linked in blogs: Linear Lists, Stacks
02-Linear Structure 1 Merging Two Sorted Linked List Sequences (15 pts)
This is a C language fill-in-the-function problem that trains the most basic linked list operations. If you know C programming, you must do this;
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node {
ElementType Data;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToNode List;
List Read(); /* 细节在此不表 */
void Print( List L ); /* 细节在此不表;空链表将输出NULL */
List Merge( List L1, List L2 );
int main()
{
List L1, L2, L;
L1 = Read();
L2 = Read();
L = Merge(L1, L2);
Print(L);
Print(L1);
Print(L2);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
List Merge( List L1, List L2 ) {
List p1,p2,p3,T;
T = (List) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
p3 = T;
p1 = L1->Next;
p2 = L2->Next;
while (p1 && p2) { //p1和p2都存在时
if (p1->Data <= p2->Data) {
p3->Next = p1;
p3 = p3->Next;
p1 = p1->Next;
} else {
p3->Next = p2;
p3 = p3->Next;
p2 = p2->Next;
}
}
if (p1) {//哪个还存在哪个后边的就全接到p3上
p3->Next = p1;
} else p3->Next = p2;
L1->Next = NULL;
L2->Next = NULL;
return T;
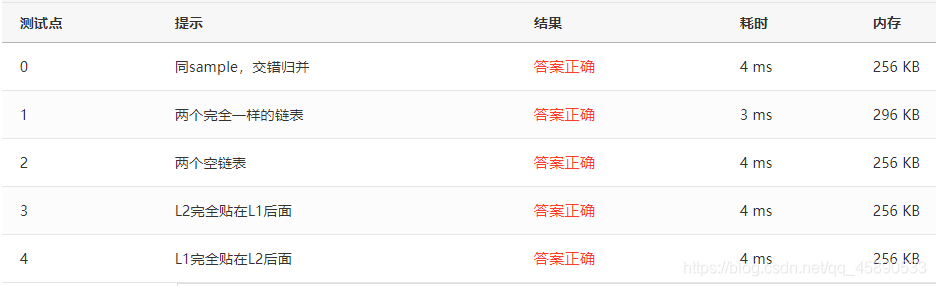
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows
02-Linear Structure 2 Polynomial Multiplication and Addition (20 pts)
This is a C language fill-in-the-function problem that trains the most basic linked list operations. If you know C programming, you must do this;
Approach
Approach: Use a linked list with a header node for storage. For addition: When comparing exponents of p1 and p2 (the two addition list pointers), if one side has a larger exponent, directly place it into p3 (tail insertion), then move the pointer of the larger side forward. If the exponents are equal, combine like terms before inserting. Note that if the coefficient is 0, do not insert it and just move both pointers forward. Finally, if one side still has remaining elements, append them directly to L3. At the end, check if L3 is empty; if so, insert a zero polynomial. For multiplication: First multiply each term in L1 by the first term of L2 to get a polynomial, then multiply each term from the second term onward in L2 by the entire L1 polynomial (multiplying and comparing/inserting as we go), or use the addition function (but it timed out when I tried it… so I didn’t use it). At the end, also check if L3 is empty; if so, insert a zero polynomial. PS: When combining like terms, if the coefficient becomes 0, it must be deleted!
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct LNode* List;
struct LNode {
ElementType factor; //系数
ElementType exmt; //指数
List next;
};
void Make_EmptyList(List Head) {
Head = new LNode;
Head->exmt = 0;
Head->factor = 0;
Head->next = NULL;
}
void E_Insert(List Head, ElementType f, ElementType e) {//尾插法插入
if(!Head) {
Make_EmptyList(Head);
}
List s = Head;
while (s->next) {//保证s是最后一个
s = s->next;
}
List p = new LNode;
p->factor = f;
p->exmt = e;
p->next = NULL;
s->next = p;
}
void H_Insert(List Head, ElementType f, ElementType e) {//头插法插入
if(!Head) {
Make_EmptyList(Head);
}
List p = new LNode;
p->factor = f;
p->exmt = e;
p->next = Head->next;
Head->next = p;
}
void PrintList(List Head) {
List p = Head->next;
cout << p->factor << " " << p->exmt;
p = p->next;
while (p) {
cout << " " << p->factor << " " << p->exmt;
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Clear_List(List Head) {
List p1 = Head->next;
while(p1){
List p2 = p1->next;
delete p1;
p1 = p2;
}
}
List AddList(List L1, List L2) {
if (!L1->next) return L2;
if (!L2->next) return L1;
List A = new LNode;
A->next = NULL;
List p1 = L1->next;
List p2 = L2->next;
if(p1->exmt == 0 && p1->factor == 0) return L2;
if(p2->exmt == 0 && p2->factor == 0) return L1;
List p3 = A;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1->exmt > p2->exmt) {
if(p1->factor != 0)
E_Insert(A, p1->factor, p1->exmt);
p1 = p1->next;
}
else if (p1->exmt < p2->exmt) {
if(p2->factor != 0)
E_Insert(A, p2->factor, p2->exmt);
p2 = p2->next;
} else { //p1->exmt == p2->exmt
int f = p1->factor + p2->factor;
int e = p1->exmt;
if(f != 0)
E_Insert(A, f, e);
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
}
while (p3->next) {
p3 = p3->next;
}
if (p1) {//哪个还存在哪个后边的就全接到p3上
p3->next = p1;
} else p3->next = p2;
if(!A->next) {
E_Insert(A, 0, 0);
}
return A;
}
List MultiplyList(List L1, List L2) {
List L3 = new LNode;
L3->next = NULL;
List p1 = L1->next;
List p2 = L2->next;
List p3 = L3->next;
if (!p1 || !p2) {
E_Insert(L3, 0, 0);
return L3;
}
while (p1) { //L1中的每一项乘L2的第一项
int f, e;
f = p1->factor * p2->factor;
e = p1->exmt + p2->exmt;
if(f != 0)
E_Insert(L3, f, e);
p1 = p1->next;
}
// L2中的每一项乘以L1中一整个多项式
while (p2->next) { //L2中的每项p2
p1 = L1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
while (p1) { //L1中的每一项 * p2
int f, e;
f = p1->factor * p2->factor;
e = p1->exmt + p2->exmt;
if(f == 0) {
p1 = p1->next;
continue;
}
p3 = L3;
while (p3->next && p3->next->exmt > e) {
p3 = p3->next;
}
List np = p3->next;//np->exmt <= e
if (!np) {
np = new LNode;
np->exmt = e;
np->factor = f;
np->next = NULL;
p3->next = np;
}
else if (np->exmt < e) {
List p = new LNode;
p->exmt = e;
p->factor = f;
p->next = np;
p3->next = p;
}
else {
np->factor += f;
if(np->factor == 0) {//合并同类项后为0 删除这个
p3->next = np->next;
delete np;
}
} //np->exmt == e
p1 = p1->next;
}
}
if(!L3->next) {
E_Insert(L3, 0, 0);
}
return L3;
}
int main() {
List L1, L2, L3, L4;
int n1, n2, f, e;
cin >> n1;
L1 = new LNode;
L1->next = NULL;
L2 = new LNode;
L2->next = NULL;
L3 = new LNode;
L3->next = NULL;
L4 = new LNode;
L4->next = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i) {
cin >> f >> e;
E_Insert(L1, f, e);
}
cin >> n2;
for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i) {
cin >> f >> e;
E_Insert(L2, f, e);
}
L3 = MultiplyList(L1, L2);
L4 = AddList(L1, L2);
PrintList(L3);
PrintList(L4);
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows. Although there are few, they kept me stuck for half a day lol

02-Linear Structure 3 Reversing Linked List (25 pts)
Adapted from a well-known company’s written test, this is a 2014 Spring PAT exam problem. Not difficult, give it a try;
Problem Description
Given a constant K and a linked list L, you should reverse every K elements on L. For example, given L as 1->2->3->4->5->6 If K=3, then you must output 3->2->1->6->5->4 If K=4, you must output 4->3->2->1->5->6. Input Specification: Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, the total number of nodes N (<= 10^5), and a positive K (<= N) which is the length of the sublist to be reversed. A node address is a 5-digit non-negative integer, and NULL is represented by -1. Then N lines follow, each describing a node in the format: Address Data Next Where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer, and Next is the position of the next node. Output Specification: For each case, output the resulting ordered linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as the input.
Sample Input:
00100 6 4 00000 4 99999 00100 1 12309 68237 6 -1 33218 3 00000 99999 5 68237 12309 2 33218
Sample Output:
00000 4 33218 33218 3 12309 12309 2 00100 00100 1 99999 99999 5 68237 68237 6 -1
Approach
Use structs to store data, use arrays to store index references. When reversing, we only need to reverse the array elements, which can be done using the reverse function from the algorithm library.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxsize 100002
struct LNode {
int Data;
int Next;
}a[maxsize];
int list[maxsize];//每个结点的地址
int Head,N,K,p;//第一个节点地址,所有结点数,翻转子序列长度
int main() {
cin >> Head >> N >> K;
list[0] = Head;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int index, data, next;
cin >> index >> data >> next;
a[index].Data = data;
a[index].Next = next;
}
p = a[Head].Next;
int sum = 1;
while(p != -1) {
list[sum++] = p;
p = a[p].Next;
}
int j = 0;
while(j + K <= sum) {
reverse(&list[j], &list[j+K]);
j = j + K;
}
for(int i = 0; i < sum-1; ++i) {
int id = list[i];//第i个结点的索引
printf("%05d %d %05d\n", id, a[id].Data, list[i+1]);
}
printf("%05d %d -1\n", list[sum-1], a[list[sum-1]].Data);
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows

02-Linear Structure 4 Pop Sequence (25 pts)
This is a 2013 Spring PAT exam problem, testing the understanding of basic stack concepts. You should give it a try.
Problem Description
Given a stack that can hold at most M numbers, push N numbers 1, 2, 3, …, N and pop them randomly. You should tell if a given sequence of numbers is a possible pop sequence of the stack. For example, if M is 5 and N is 7, we can obtain 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 from the stack, but not 3, 2, 1, 7, 5, 6, 4. Input Specification: Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 3 numbers (all no more than 1000): M (the maximum capacity of the stack), N (the length of the push sequence), and K (the number of pop sequences to check). The next K lines each contain a pop sequence of N numbers. All numbers in a line are separated by spaces. Output Specification: For each pop sequence, print “YES” in one line if it is indeed a possible pop sequence of the stack, or “NO” if not.
Sample Input:
5 7 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 2 1 7 5 6 4 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 6 4 3 7 2 1 1 7 6 5 4 3 2
Sample Output:
YES NO NO YES NO
Approach
When processing each sequence, first push 1 onto the stack. For each number x read, compare it with the top element. If x is greater than the top element, push numbers until x-1. If x equals the top element, pop directly. If x is less than the top element, it’s directly false. If the stack is empty, a number needs to be pushed. If it overflows, it’s also false.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define maxsize 100002
int s[maxsize];//堆栈
int top;//栈顶元素下标 0的时候为空堆栈
int M, N, K;//栈容量,序列长度,几个序列
void s_clear() {
top = 0;
memset(s, 0, maxsize);
}
int s_pop() {
int x = s[top];
s[top] = 0;
top--;
return x;
}
void s_push(int x) {
top++;
s[top] = x;
}
bool judge() {
bool ans = true;
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
if (top == 0) {//堆栈为空
s_push(k++);
}
if (x < s[top]) {
ans = false;
} else if (x == s[top]) {
s_pop();
} else { //若大于栈顶元素
while (k <= x - 1) {
s_push(k++);
}
s_push(k++);
if (top > M) ans = false;
s_pop();
}
if (k > N + 1) ans = false;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> M >> N >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
s_clear();
if (judge()) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
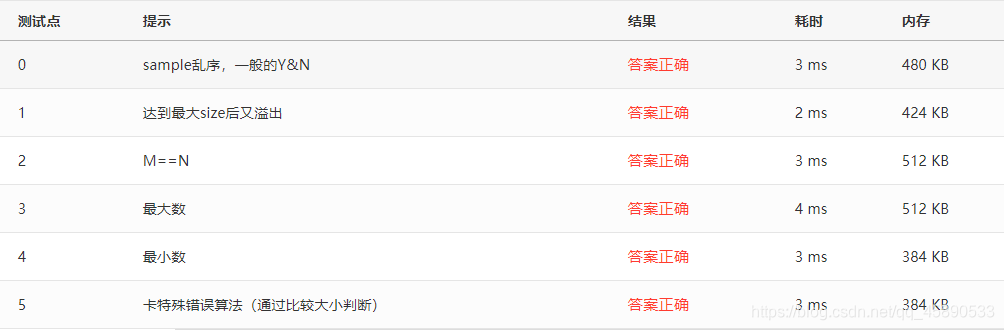
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows, passed on the first try

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~