This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
Problem Set Master Index Study reference blog: Data Structure Study Notes <9> Hash Search
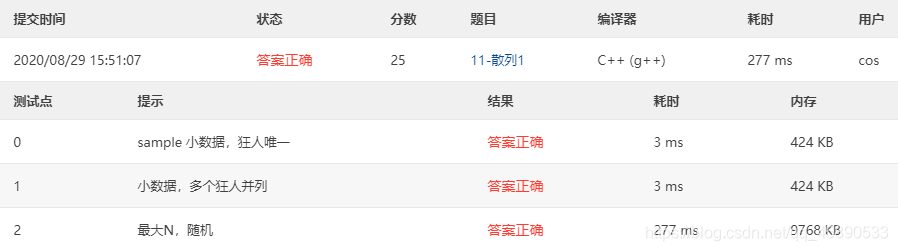
11-Hash 1 Phone Chat Addict (25 pts)
A must-do. If you don’t know where to start, you can watch the “Beginner Session”, which will explain the C implementation in detail.
Approach
Hash search. During insertion, if the key already exists, just modify the operation accordingly. Directly use the previous template.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
const int MaxSize = 100000;
typedef int Index;//散列后的下标
//散列单元状态类型,分别对应:有合法元素、空单元、有已删除元素
typedef enum {Legitimate, Empty, Deleted} EntryType;
struct Person {
string str;
int num;
bool operator!=(const Person& p) {
return str != p.str;
}
} per;
typedef Person DataType;//数据的类型
struct HashNode { //散列表单元类型
DataType data; //存放元素
EntryType flag; //单元状态
};
struct HashTable { //散列表类型
int TableSize; //表长
HashNode *Units; //存放散列单元的数组
};
typedef HashTable *ptrHash;
//返回大于N且不超过MaxSize的最小素数,用于保证散列表的最大长度为素数
int NextPrime(int N) {
int i, p = (N%2) ? N+2 : N+1;//从大于N的下一个奇数p开始
while(p <= MaxSize) {
for(i = (int)sqrt(p); i > 2; i--)
if(!(p %i)) break;//不是素数
if(i == 2) break;//for正常结束,是素数
else p += 2;//试探下一个奇数
}
return p;
}
//创建一个长度大于TableSize的空表。(确保素数)
ptrHash CreateTable(int TableSize) {
ptrHash H;
int i;
H = new HashTable;
H->TableSize = NextPrime(TableSize);
H->Units = new HashNode[H->TableSize];
for(int i = 0; i < H->TableSize; ++i)
H->Units[i].flag = Empty;
return H;
}
//返回经散列函数计算后的下标
Index Hash(DataType Key, int TableSize) {
unsigned int h = 0; //散列函数值,初始化为0
string str = Key.str;
int len = str.length();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
h = (h << 5) + str[i];
return h % TableSize;
}
//查找Key元素,这里采用平方探测法处理冲突
Index Find(ptrHash H, DataType Key) {
Index nowp, newp;
int Cnum = 0;//记录冲突次数
newp = nowp = Hash(Key, H->TableSize);
//若该位置的单元非空且不是要找的元素时发生冲突
while(H->Units[newp].flag != Empty && H->Units[newp].data != Key) {
++Cnum;//冲突增加一次
if(++Cnum % 2) {
newp = nowp + (Cnum+1)*(Cnum+1)/4;//增量为+i^2,i为(Cnum+1)/2
if(newp >= H->TableSize)
newp = newp % H->TableSize;
} else {
newp = nowp - Cnum*Cnum/4;//增量为-i^2,i为Cnum/2
while(newp < 0)
newp += H->TableSize;
}
}
return newp;//返回位置,该位置若为一个空单元的位置则表示找不到
}
//插入Key到表中
bool Insert(ptrHash H, DataType Key) {
Index p = Find(H, Key);
if(H->Units[p].flag != Legitimate) {
H->Units[p].flag = Legitimate;
Key.num = 1;
H->Units[p].data = Key;
return true;
} else {//该键值已存在
H->Units[p].data.num++;
return false;
}
}
int main() {
int N;
cin >> N;
N *= 2;
ptrHash H = CreateTable(N+1);
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> per.str;
Insert(H, per);
}
string minstr;
int maxnum = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < H->TableSize; ++i) {
HashNode h = H->Units[i];
if(h.flag != Legitimate) continue;
if(h.data.num > maxnum) {//有更狂的
sum = 1;
minstr = H->Units[i].data.str;
maxnum = H->Units[i].data.num;
} else if(h.data.num == maxnum) {
sum++;
if(h.data.str < minstr) minstr = h.data.str;
}
}
if(sum == 1) {
cout << minstr << ' ' << maxnum << endl;
} else cout << minstr << ' ' << maxnum << ' ' << sum << endl;
return 0;
}Test Cases
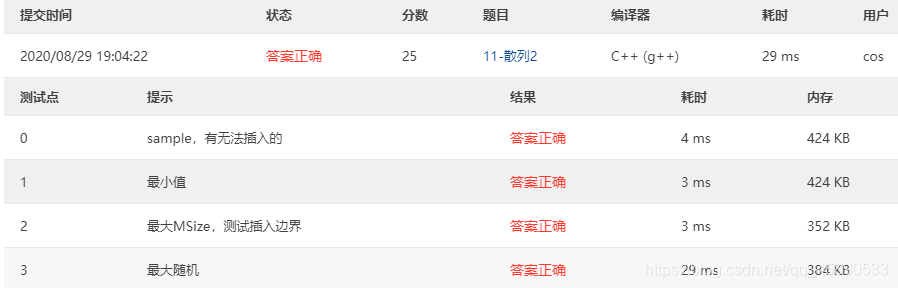
11-Hash 2 Hashing (25 pts)
2014 graduate school entrance exam real problem. Quite straightforward, a must-do.
Approach
There are a few pitfalls: 1 is not a prime number, so special handling is needed if M is 1. Since there are no deletion operations in this problem and we only need to output indices, we just need to maintain an array to mark whether a position has been used.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100005;
typedef long long ll;
int TableSize;
bool a[maxn];
bool isPrime(int m) {
if(m <= 1) return false;
int k = (int)sqrt(m);
for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i) {
if(m % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
int NextPrime(int m) {
if(m % 2 == 0 || m == 1)
m++;
while(!isPrime(m)) m += 2;
return m;
}
int Hash(int x) {
return x % TableSize;
}
void Insert(int x) {
int p = Hash(x);
if(!a[p]) { //该位置没有元素
a[p] = true;
cout << p;
} else {
int newp = p;
int i;
for(i = 1; i <= TableSize; ++i) {
newp = (p+i*i) % TableSize;
if(!a[newp]) {
a[newp] = true;
cout << newp;
return;
}
}
cout << '-';
}
}
int main() {
int M, N, x;
cin >> M >> N;
TableSize = NextPrime(M);
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> x;
Insert(x);
if(i == N-1) cout << endl;
else cout << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
Test Cases
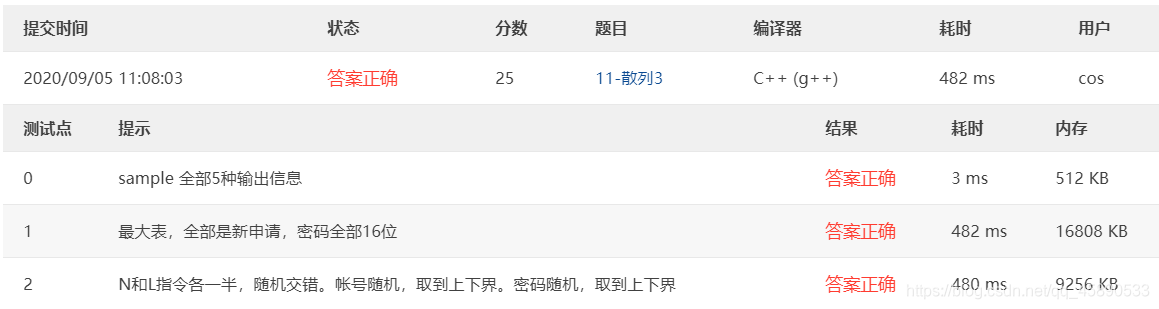
11-Hash 3 QQ Account Registration and Login (25 pts)
A textbook exercise on data structures. Can be done with hashing or sorting. If you’re interested and have time, try both approaches. Optional.
Problem Summary
Implement a simplified version of QQ account registration and login functionality. The main task is to check whether an account exists and whether the password matches.
Approach
Initially used regular hash search with bit-shifting and quadratic probing, but the last two test cases kept failing, so I switched to using STL’s map instead…
Code
Using STL’s map, the solution is very concise.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, string> user;//账号密码
int N;
string o, us, pw;
cin >> N;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> o >> us >> pw;
if(o == "L") {//Login
if(user.find(us) == user.end())
cout << "ERROR: Not Exist" << endl;
else if(user[us] == pw)
cout << "Login: OK" << endl;
else cout << "ERROR: Wrong PW" << endl;
} else if(o == "N") {//New
if(user.find(us) != user.end())
cout << "ERROR: Exist" << endl;
else {
user[us] = pw;
cout << "New: OK" << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}Test Cases
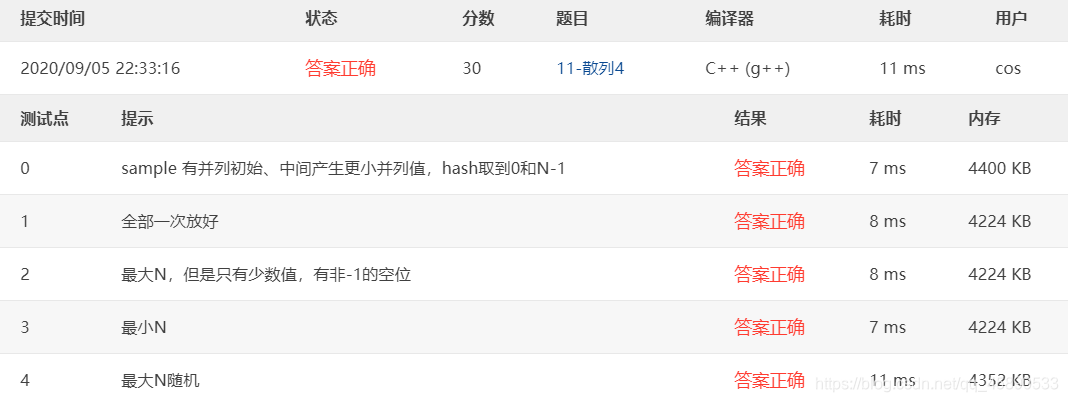
11-Hash 4 Hashing - Hard Version (30 pts)
A very interesting problem. It requires some thinking — once you figure it out, it becomes very easy. So take some time to think about it if you can. If you really can’t figure it out, don’t worry, it will be explained in the next problem session.
Problem Summary
- Given hash function H(x) = x%N and linear probing for collision resolution
- Given the hash mapping result, determine the input order
- When element x is mapped to position H(x) and finds that position already occupied by y, then y must have been inserted before x
Approach
Topological sort! It’s actually a combination of hash mapping and topological sorting.
Code
Note a pitfall: when multiple elements have zero in-degree (i.e., the order is ambiguous), output the smallest one first. So a priority queue is used instead of a min-heap for storage, and a map is used to record the corresponding indices.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1005;
int N;
int a[maxn], In[maxn];
int edge[maxn][maxn];
map<int, int> HashIndex;
void Topsort() {//拓扑排序
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if(edge[i][j] == 1) {
In[j]++;
}
}
}
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if(In[i] == 0 && a[i] >= 0) {
q.push(a[i]);
}
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int num = q.top();
q.pop();
cout << num;
int v = HashIndex[num];
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if(v == i || edge[v][i] == -1) continue;//检查以v为起点的所有边
if(--In[i] == 0) q.push(a[i]);
}
if(q.empty()) cout << endl;
else cout << " ";
}
}
int main() {
memset(edge, -1, sizeof(edge));
memset(In, 0, sizeof(In));
cin >> N;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
cin >> a[i];
HashIndex[a[i]] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if(a[i] < 0) continue;
int Hash = a[i] % N;
if(a[Hash] >= 0 && a[Hash] != a[i]) {//该位置已被占有
for(int j = Hash; j != i; j = (j+1) % N) {
edge[j][i] = 1;
}
}
}
Topsort();
return 0;
}Test Cases
KMP String Pattern Matching (25 pts)
You can test various pattern matching algorithms you find here and see how they perform.
Approach
Nothing much to say, just KMP and done.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define div 1000000007
const int maxn = 1000005;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f;
int N,M;
int nxt[maxn];
void getnxt(string t) {
int len = t.length();
int i = 0, j = -1;
nxt[0] = -1;
while (i < len) {
if (j == -1 || t[i] == t[j]) {
i++, j++;
if (t[i] == t[j])
nxt[i] = nxt[j]; // next数组优化
else
nxt[i] = j;
} else
j = nxt[j];
}
}
int KMP(string s, string t) {//s为文本串,t为模式串(短的那个)
getnxt(t);
int len1 = s.length();
int len2 = t.length();
int i = 0, j = 0, ans = 0;
while (i < len1) {
if (j == -1 || s[i] == t[j]) {
i++, j++;
if (j >= len2) {
return i-j;
}
} else
j = nxt[j];
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
string String, Pattern;
cin >> String;
cin >> N;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
memset(nxt, 0, sizeof(nxt));
cin >> Pattern;
int k = KMP(String, Pattern);
if(k == -1) cout << "Not Found" << endl;
else cout << String.substr(k) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Test Cases

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~