This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
Problem Set Master Index Study reference blog: Graph Theory
07-Graph 4 Harry Potter’s Exam (25 pts)
This is a very basic algorithm application, a must-do. If you don’t know how, check out the beginner session, which will explain the C implementation in detail.
Problem Summary
Given the spell lengths required between every pair of animals, Harry Potter should bring the animal to the exam that minimizes the total spell length for the hardest transformation. Output the animal number Harry Potter should bring to the exam and the length of the longest transformation spell.
Approach
Use the Floyd algorithm to obtain the shortest path matrix dist (dist[i][j] represents the shortest length from i to j). In each row, find the hardest transformation (i.e., the maximum dist[i][j]), then among these elements find the minimum. Output the index i of the minimum and its value.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1005;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f;
int N,M,x,y,z;
bool visited[maxn];
int dist[maxn][maxn];
//用Floyd算法得到最短路矩阵
//让最难变的动物咒语长度最小
void init() {
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
dist[i][j] = inf;
}
dist[i][i] = 0;
}
}
void Floyd() {
for(int k = 1; k <= N; ++k) {
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
int num,ans,hardest;
ans = inf+1;
Floyd();
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
hardest = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
if(dist[i][j] > hardest) {
hardest = dist[i][j];
}
}
if(hardest == inf) {
printf("0");
return;
}
if(hardest < ans) {
num = i;
ans = hardest;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", num, ans);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
init();
for(int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &z);
dist[x][y] = dist[y][x] = z;
}
solve();
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows:
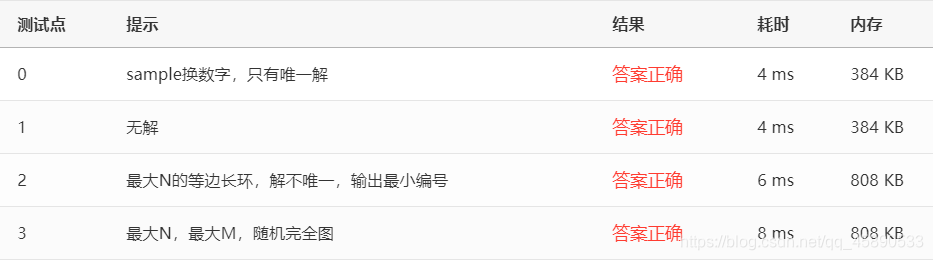
07-Graph 5 Saving James Bond - Hard Version (30 pts)
If you have the energy, be a good person to the end. If you already tried saving 007 last week, continue giving him advice this week.
Problem Summary
Output the minimum number of jumps and the xy coordinates of the crocodiles along the jumping path.
Approach
Use the Floyd algorithm to obtain the shortest path matrix edge (edge[i][j] represents the minimum number of jumps from crocodile i to crocodile j; initialized to 1 if a jump is possible, 0 otherwise), while using path to store the route. Note: if there are many shortest paths, only output the path with the smallest first jump.
Code
// 07-图5 Saving James Bond - Hard Version (30分)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 105;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f;
int N,D;
bool vis[maxn];
int edge[maxn][maxn];
int path[maxn][maxn];
struct Point {
int x, y;
bool visited;
} v[maxn],s;
struct Fjump{
int id;
double d;
bool operator<(const Fjump& f) {
return d < f.d;
}
};
vector<Fjump> fj;
void init() {
for(int i = 0; i <= N+1; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j <= N+1; ++j) {
edge[i][j] = inf;
path[i][j] = -1;
}
edge[i][i] = 0;
}
}
double countDist(Point a, Point b) {
return sqrt(pow((a.x-b.x),2) + pow((a.y-b.y),2));
}
bool check(Point a) {
int s = 50 - D;
if(abs(a.x) >= s || abs(a.y) >= s)
return true;
else return false;
}
void Floyd() {
for(int k = 1; k <= N; ++k) {
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
if(edge[i][k] + edge[k][j] < edge[i][j]) {
edge[i][j] = edge[i][k] + edge[k][j];
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
}
bool firstJump(int i) {
double d = countDist(s,v[i]);
d -= 7.5;
return d <= D;
}
void PrintPath(int S, int E) {
if(path[S][E] != -1) {
int k = path[S][E];
PrintPath(S,k);
printf("%d %d\n", v[k].x, v[k].y);
PrintPath(k,E);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
scanf("%d %d", &N, &D);
init();
v[0].visited = false;
v[0].x = v[0].y = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d", &v[i].x, &v[i].y);
v[i].visited = false;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
if(countDist(v[i],v[j]) <= D)
edge[i][j] = edge[j][i] = 1;
}
}
Floyd();
int mind,temp;
int S,E;
mind = inf;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
if(firstJump(i)) {
Fjump f;
f.d = countDist(s, v[i]);
f.id = i;
fj.push_back(f);
}
}
sort(fj.begin(), fj.end());
for(int i = 0; i < fj.size(); ++i) {
int sa = fj[i].id;
if(check(v[sa])) {
S = sa;
E = sa;
mind = 2;
break;
}
for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) {
if(sa == j) continue;
if(check(v[j])) {
temp = 2 + edge[sa][j];
if (temp < mind) {
S = sa;
E = j;
mind = temp;
}
}
}
}
if(D >= 42.5) { //一步上岸
printf("1\n");
} else if (mind != inf) {
printf("%d\n", mind);
if(S == E) {
printf("%d %d\n", v[S].x, v[S].y);
} else {
printf("%d %d\n", v[S].x, v[S].y);
PrintPath(S,E);
printf("%d %d\n", v[E].x, v[E].y);
}
} else
printf("0\n");
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows:
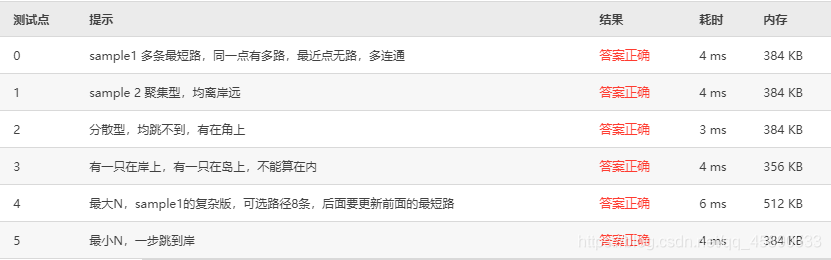
07-Graph 6 Travel Planning (25 pts)
A variation of Dijkstra’s algorithm — this is all the professor can help you with, think about how to modify the classic algorithm to solve this problem on your own. If you really can’t figure it out, don’t worry, the algorithm will be covered next week.
Problem Summary
Given the highway distances and costs between all villages, calculate and output the minimum distance and corresponding cost between two given villages. If there are multiple shortest paths, output the one with the minimum cost.
Approach
A variation of Dijkstra’s algorithm. Simply store both distance and cost for each edge, add an additional cost array, and update cost at the same time as updating dist.
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 505;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f;
int N,M,S,D,u,v,len,p;
struct Edge {
int len, pay;
}e[maxn][maxn];
int dist[maxn];
int cost[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void init() {
for(int i = 0; i <= N; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j <= N; ++j) {
e[i][j].pay = e[i][j].len = inf;
}
e[i][i].pay = e[i][i].len = 0;
}
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
}
void Dijstra(int u) {
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
dist[i] = e[u][i].len;
cost[i] = e[u][i].pay;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
int t, mindis = inf;
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if(!vis[j] && dist[j] <= mindis) {
mindis = dist[j];
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if(vis[j] || e[t][j].len == inf) continue;
if(dist[j] > e[t][j].len + dist[t]) {
dist[j] = e[t][j].len + dist[t];
cost[j] = e[t][j].pay + cost[t];
} else if(dist[j] == e[t][j].len + dist[t]) {
if(cost[j] > e[t][j].pay + cost[t]) {
cost[j] = e[t][j].pay + cost[t];
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &N, &M, &S, &D);
init();
while(M--) {
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &u, &v, &len, &p);
e[u][v].len = e[v][u].len = len;
e[u][v].pay = e[v][u].pay = p;
}
Dijstra(S);
printf("%d %d\n", dist[D], cost[D]);
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows:
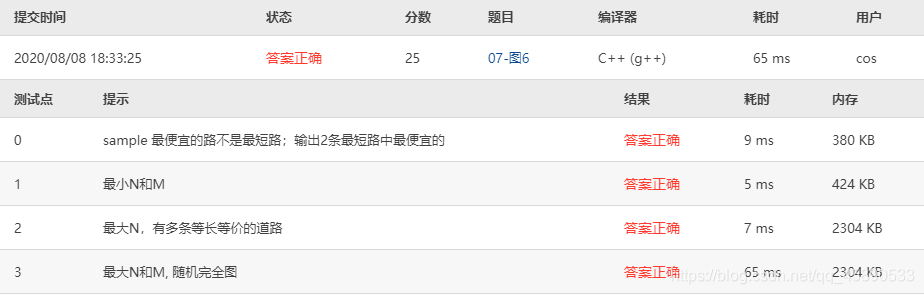

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~