This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
01-Complexity 1 Maximum Subsequence Sum Problem (20 pts)
This is the experiment problem for the 4 algorithms covered at the end of this lesson. It is a basic requirement and must be done;
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, x, nowsum, maxsum;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> x;
nowsum += x;
if (nowsum > maxsum) {
maxsum = nowsum;
} else if(nowsum <= 0) {
nowsum = 0;
}
}
cout << maxsum << endl;
return 0;
}Test Cases
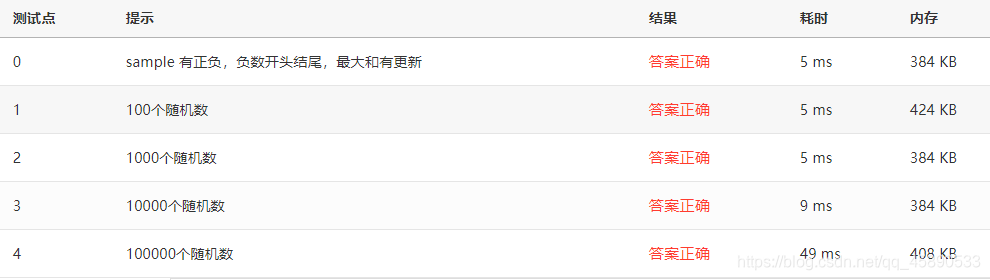
01-Complexity 2 Maximum Subsequence Sum (25 pts)
This is a 2004 Zhejiang University Computer Science graduate re-examination problem. Requirements are slightly higher, optional.;
Problem Description
The problem asks to find the maximum subsequence sum, as well as the first and last numbers of the maximum subsequence. Note that if there are multiple maximum subsequences, take the one with the smallest index.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 10002
int n, x, nowsum, maxsum, l, r, first,last;
int a[N];
int main() {
bool allminus = true;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
maxsum = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (a[i] >= 0)
allminus = false;
nowsum += a[i];
if (nowsum > maxsum && nowsum >= 0) {//最大,更新maxsum和r
maxsum = nowsum;
r = i;
first = l;
last = r;
} else if(nowsum < 0) {
nowsum = 0;
l = r = i+1;
}
}
if (allminus) {
cout << 0 << " " << a[0] << " " << a[n-1] << endl;
} else cout << maxsum << " " << a[first] << " " << a[last] << endl;
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows; cases 5 and 6 are error-prone
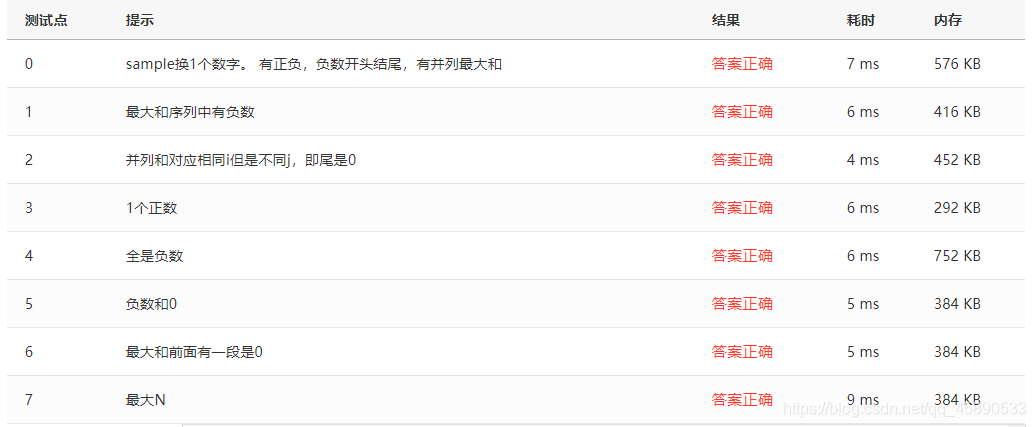
01-Complexity 3 Binary Search (20 pts)
This is a fill-in-the-function problem paired with the after-class discussion questions. If you have spare capacity and know C programming, you can give it a try. You only need to submit a function, not the main function or other functions. If you don’t know C, study the after-class discussion questions on binary search instead.
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define NotFound 0
typedef int ElementType;
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
List ReadInput(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表。元素从下标1开始存储 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P;
L = ReadInput();
scanf("%d", &X);
P = BinarySearch( L, X );
printf("%d\n", P);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X ) {
if (L->Last == 0) return NotFound;
int l, r, mid, ans;
l = 1, r = L->Last;
while(l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(L->Data[mid] == X) {
ans = mid;
return ans;
} else if(L->Data[mid] < X) {
l = mid + 1;
} else r = mid - 1;
}
return NotFound;
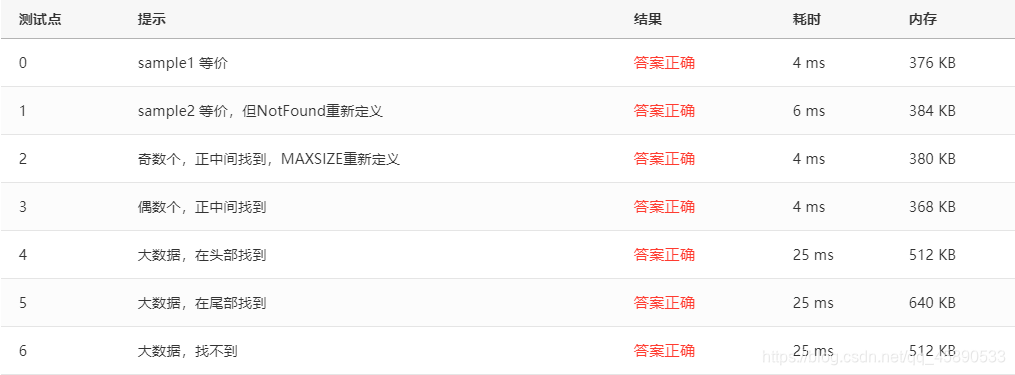
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows; case 5 is error-prone

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~