This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
Problem Set Master Index Study notes linked in blog: Heaps, Huffman Trees, and Union-Find
05-Tree 7 Path in Heap (25 pts)
The C language implementation will be introduced in the “Beginner’s Session”. This is basic min-heap construction training and must be done.
Problem Description
Given a min-heap insertion sequence and an index sequence, for each index i, output the values on the path from Data[i] to the root node.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int mindata = -10005;
const int maxsize = 10000;
typedef struct HeapStruct *MinHeap;
struct HeapStruct {
int *Data;
int Size;
};
MinHeap Create(int maxsize) {
MinHeap H = new HeapStruct;
H->Data = new int[maxsize];
H->Size = 0;
H->Data[0] = mindata;
return H;
}
void Insert(int data, MinHeap H) {
int i;
i = ++H->Size;
for(; H->Data[i>>1] > data; i >>= 1) {
H->Data[i] = H->Data[i>>1];
}
H->Data[i] = data;
}
void PrintPath(int index, MinHeap H) {
bool flag = false;
while(index != 0) {
if(flag) cout << " " << H->Data[index];
else cout << H->Data[index];
flag = true;
index >>= 1;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
MinHeap H = Create(maxsize);
int N, M, x;
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> x;
Insert(x, H);
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
cin >> x;
PrintPath(x, H);
}
return 0;
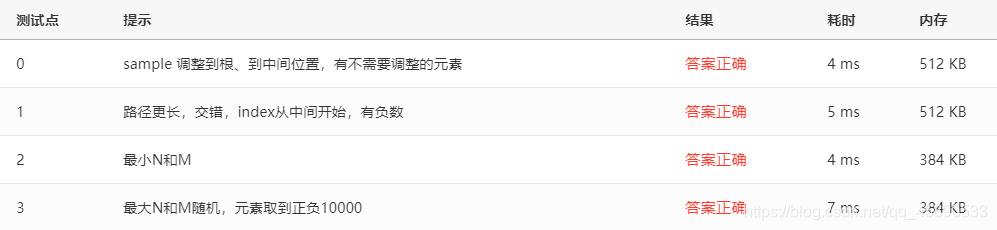
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows
05-Tree 8 File Transfer (25 pts)
About union-find. The 2005 and 2007 Zhejiang University Computer Science graduate admission exam problems were adapted from this problem. The “Beginner’s Session” introduces optimizations to the basic union-find algorithm. Give it a try after watching the lecture.
Problem Description
In each test case, C queries whether any two computers are connected, I connects the two computers, and finally after S ends, check whether all are connected. If not all connected, output how many connected components there are.
Approach
Union-Find with path compression.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10005;
int fa[maxn];
int N, x, y;
char ch;
inline void init() {
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i)
fa[i] = i;
}
int find(int x) {//查询+路径压缩 把沿途的每个节点的父节点都设为根节点
return x == fa[x] ? x : (fa[x] = find(fa[x]));
}
void Merge(int x, int y) {
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &N);
init();
getchar();
scanf("%c", &ch);
while(ch != 'S') {
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
getchar();
if(ch == 'C') {
if(find(x) == find(y)) cout << "yes" << endl;
else cout << "no" << endl;
} else if(ch == 'I') Merge(x, y);
scanf("%c", &ch);
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
if(fa[i] == i) ans++;
}
if(ans == 1) cout << "The network is connected." << endl;
else cout << "There are " << ans << " components." << endl;
return 0;
}Test Cases
Test cases are as follows

05-Tree 9 Huffman Codes (30 pts)
Tests the understanding of Huffman coding. The program may be somewhat complex, proceed according to your ability. Problem description: Given a set of characters and their frequencies, determine whether the encoding scheme provided by students is an optimal encoding.
Approach
After watching Professor Chen Yue’s explanation, I learned that the approach is: first build a Huffman tree based on the given characters and frequencies to get the optimal WPL (encoding length), then check the students’ encodings. If the lengths match, verify whether they are prefix codes. Here I used a priority queue to replace the lengthy min-heap code, and used an alternative method to calculate the WPL.


Code
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define div 1000000007
const int maxn = 70;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f;
int N,M,codelen;
struct Code {
char ch;
string s;
int f;//频率
}a[maxn];
typedef struct TreeNode* CodeTree;
struct TreeNode {
int Weight;
CodeTree Left, Right;
};
CodeTree head;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>, greater<int> > q; //优先队列代替小顶堆
int WPL() {
int wpl = 0;
while(q.size() > 1) {
int t1 = q.top();
q.pop();
int t2 = q.top();
q.pop();
wpl += (t1+t2);
q.push(t1+t2);
}
return wpl;
}
bool check() {//检查是否是前缀码
head = new TreeNode;
head->Left = head->Right = NULL;
head->Weight = -1;
CodeTree p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
string code = a[i].s;
int len = code.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (code[i] == '1') {
if (!p->Right) {
p->Right = new TreeNode;
p->Right->Left = p->Right->Right = NULL;
p->Right->Weight = -1;
}
p = p->Right;
//中途有别的结点 有前缀码
}
else {
if (!p->Left){
p->Left = new TreeNode;
p->Left->Right = p->Left->Left = NULL;
p->Left->Weight = -1;
}
p = p->Left;
}
if (p->Weight != -1) return false;
}
p->Weight = 1;
if (p->Left || p->Right) return false;
p = head;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> N;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cin >> a[i].ch >> a[i].f;
q.push(a[i].f);
}
int codelen = WPL();
cin >> M;
while(M--) {
int len = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
cin >> a[i].ch >> a[i].s;
len += a[i].f * a[i].s.length();
}
if(len == codelen && check()) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}Test Cases
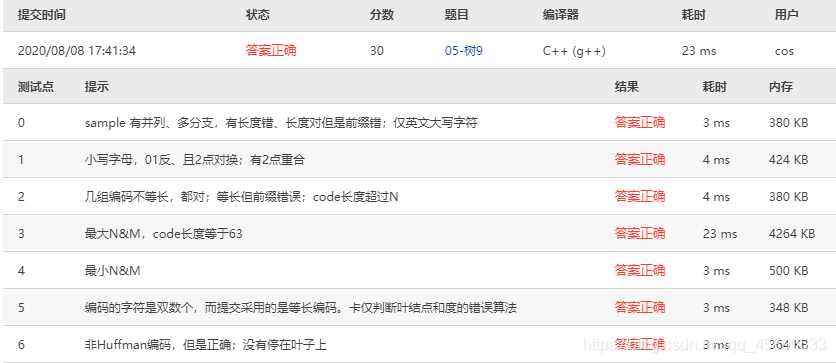
Test cases are as follows

喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~