This article has been machine-translated from Chinese. The translation may contain inaccuracies or awkward phrasing. If in doubt, please refer to the original Chinese version.
I. Abstract Data Type Description of Queues
Type name: Queue Data object set: A finite linear list with 0 or more elements Operation set: Queue Q of maximum length MaxSize belongs to Queue, queue element item belongs to ElementType
1. Create an empty queue of length MaxSize Queue CreatQueue(int MaxSize); 2. Check if queue Q is full bool IsFullQ(Queue Q, int MaxSize); 3. Insert data element item into queue Q bool AddQ(Queue Q, ElementType item); 4. Check if queue Q is empty bool IsEmptyQ(Queue Q); 5. Delete and return the front element ElementType DeleteQ(Queue Q);
II. Sequential Storage Implementation of Queues
1. Definition
The sequential storage structure of a queue typically consists of a one-dimensional array, a variable front recording the position of the queue head element, and a variable rear recording the position of the queue tail element. By wrapping the array around, it becomes a ring, forming a circular queue. To distinguish between empty and full states, a circular queue uses only n-1 array spaces.

typedef struct QNode *Queue;
struct QNode {
ElementType Data[MaxSize];//一维数组
int rear;//记录队列尾元素位置
int front;//记录队列头元素位置
int MaxSize;
//实际上front指向的是队列头元素下标的前一个
};2. Operations
(1) Creating a Circular Queue (CreateQueue)
Queue CreateQueue( int MaxSize ) {
Queue Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(struct QNode));
Q->Data = (ElementType *)malloc(MaxSize * sizeof(ElementType));
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
Q->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return Q;
}(2) Checking if Queue is Full (IsFull)
bool IsFull( Queue PtrQ ) {//front和rear+1的取余相等时队列满
return ((PtrQ->rear+1) % PtrQ->MaxSize == PtrQ->front);
}(3) Enqueue (AddQ)
Must check if the queue is full before enqueuing.
bool AddQ(Queue PtrQ, ElementType item) {
if ( IsFull(PtrQ) ) {
printf("队列满");//front和rear+1的取余相等时队列满
return false;
} else {
PtrQ->rear = (PtrQ->rear+1) % PtrQ->MaxSize;
//移动队尾rear 以取余运算来实现循环
PtrQ->Data[PtrQ->rear] = item;
return true;
}
}(4) Checking if Queue is Empty (IsEmpty)
bool IsEmpty(Queue PtrQ) {
return ( PtrQ->front == PtrQ->rear );
}(5) Dequeue (DeleteQ)
Check if the queue is empty before dequeuing.
ElementType DeleteQ(Queue PtrQ) {
if(IsEmpty(PtrQ)) {//rear和front相等时队列空
printf("队列空");
return false;
} else {
PtrQ->front = (PtrQ->front+1) % PtrQ->MaxSize;//移动队首front
return PtrQ->Data[PtrQ->front];
}
}III. Linked Storage Implementation of Queues
1. Definition
The linked storage structure of a queue can also be implemented using a singly linked list, where insertion and deletion are performed at the two ends of the list. The queue pointer front should point to the head of the linked list.
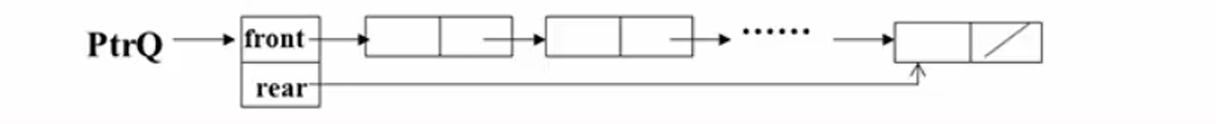
struct Node {
ElementType Data;
struct Node * Next;
}
struct QNode {//链队列结构
struct Node *rear; //指向队尾结点
struct Node *front; //指向队头结点
};
typedef struct QNode *Queue;
Queue PtrQ;2. Operations
(1) Linked Queue Initialization without Header Node (CreateQueue)
Queue CreateQueue() {
Queue Q;
Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(struct QNode));
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;//两个指针都为空
return Q;
}(2) Linked Queue Enqueue Operation without Header Node
bool AddQ(Queue PtrQ, ElementType item) {
struct Node *RearCell = PtrQ->rear;//指向队尾元素的指针
struct Node *Temp = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
Tmp->Data = X;
Tmp->Next = NULL;
if ( PtrQ->front == NULL ) {//队列为空 进第一个元素
PtrQ->rear = PtrQ->front = Tmp;
} else {
RearCell->Next = Tmp;
PtrQ->rear = Tmp;
}
return true;
}(3) Linked Queue Dequeue Operation without Header Node
ElementType DeleteQ(Queue PtrQ) {
struct Node * FrontCell;
ElementType FrontElem;//队首元素的值
if (PtrQ->front == NULL) {//1.先判断是否为空 为空无法进行出队操作
printf("队列空");
return ERROR;
}
FrontCell = PtrQ->front;
if(PtrQ->front == PtrQ->rear) //若队列只有一个元素 则删除后队列置为空
PtrQ->front = PtrQ->rear = NULL;
else
PtrQ->front = FrontCell->Next;
FrontElem = FrontCell->Data;
free(FrontCell); //释放被删除结点的空间
return FrontElem;
}
喜欢的话,留下你的评论吧~